Measuring data from generative chatbots
Generative Chatbots like Perplexity and ChatGPT successfully display links to specific products, categories, or forum articles – either in their responses or as sources. The need to appear in the answer provided by a chatbot, to obtain additional organic traffic, is the first step.
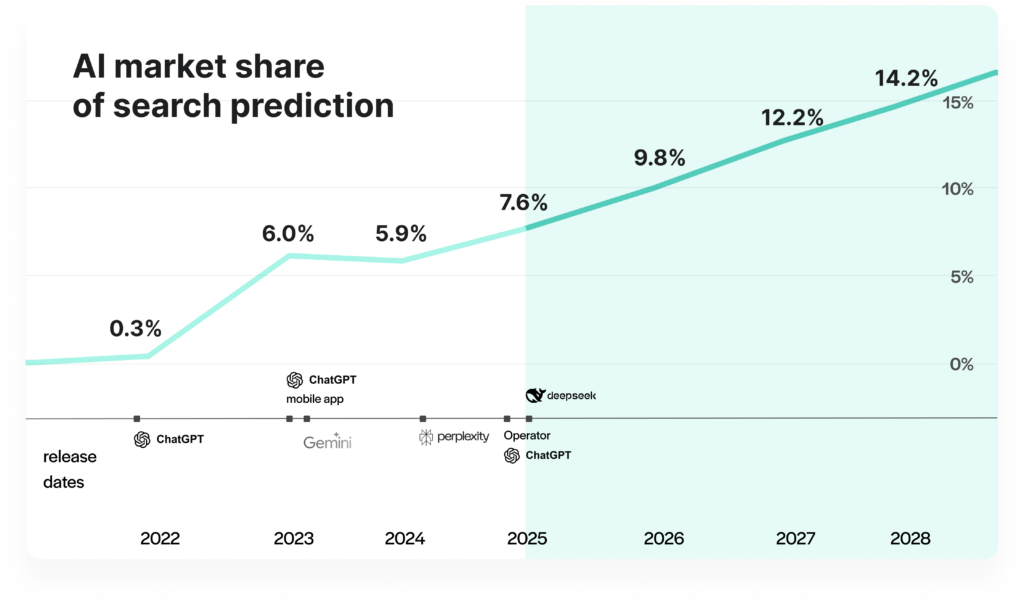
After all, their popularity is growing. At the end of 2024, only ChatGPT was receiving 3.8 billion visits per month. And, according to the research by Gartner, by the end of 2028 even 28% more users than today will pick generative AI platforms instead of traditional web search as the first step of their online research.
Making an effort to be present in the AI chat responses is crucial. But the second and most important step is measuring the effectiveness of the activities you’ve performed to get there. This is significant because it allows you to assess ROAS and the validity of investing in this new traffic channel.
The problem is, in Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools (We’ll come back to this later ;)) we cannot find accurate data on queries appearing in the chats, which is what we got used to from the perspective of classic SEO.
Therefore, it is necessary to develop methods that will allow us to measure how often, for which phrases, and with what impact on business a given brand is displayed in ChatGPT, Perplexity or Copilot.
Here’s more about some of the available measuring tools and methods, and how to combine the data we get from them to obtain some actionable insights.

Bing Webmaster Tools
Bing tells us that the data shown in Search Performance does not apply to generative chats.

At the same time, the “Internet and chat” item is visible in the data filtration:
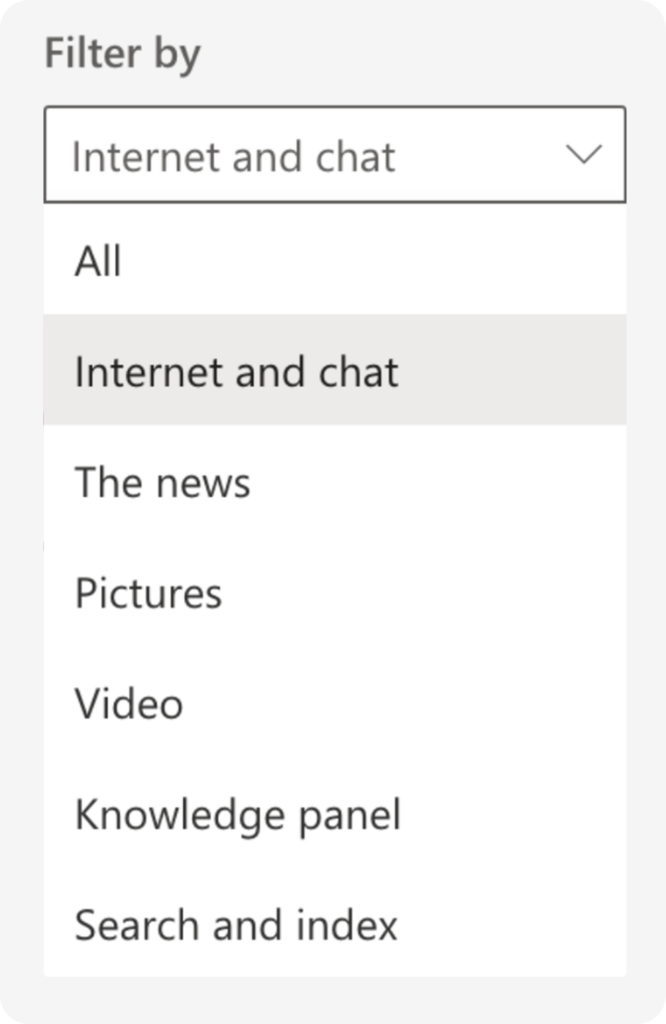
Our research indicates, however, that data from chats, although extremely anonymized, can be displayed in Bing Webmaster Tools.
Here’s an example of an exact query tested by us for one of our clients, and the results we got:
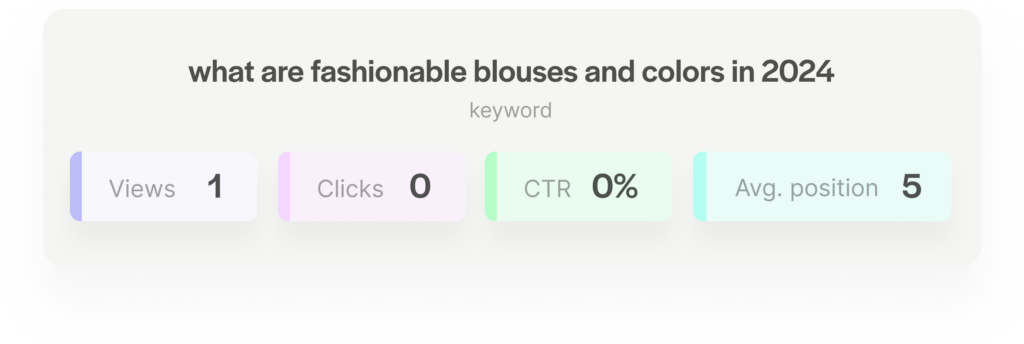
The number of views isn’t impressive, but it’s there. In our tests, though, the link to the client’s website was displayed many more times. And we were actually clicking on the link, which was not captured by the tool at all. Nevertheless, this is an indication that some data from chats appear in Bing Webmaster Tools, but in such a limited form that makes it unsuitable for efficiency analysis.
Google Analytics 4 (GA4)
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) and Looker Studio (formerly Google Data Studio) come to the rescue, allowing for deep analysis and optimization of activities in the area of AI Search Optimization.
We can perform research on the effectiveness of a given brand’s views in the generative chatbots thanks to specific sources/mediums added to the URL data mentioned during chat conversations. Even if the data may be not 100% accurate, due to the CookieConsent, – it is still giving us an indication of i.e. growing share in organic traffic for the website.
Example from ChatGPT:
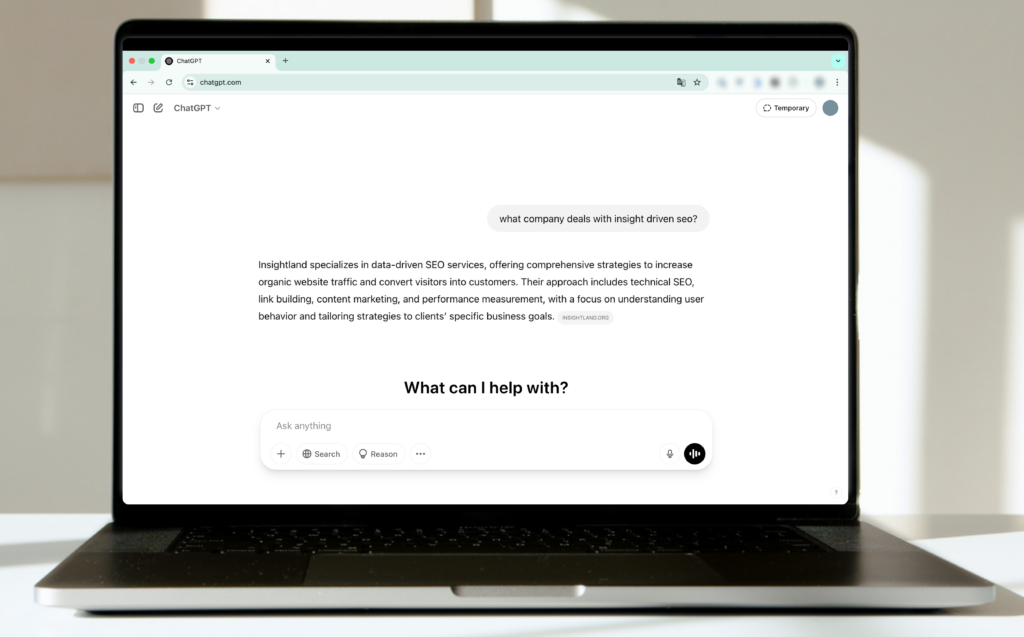
Alternatively, ChatGPT and Perplexity send data about views, e.g. using the mentioned referral attributes.
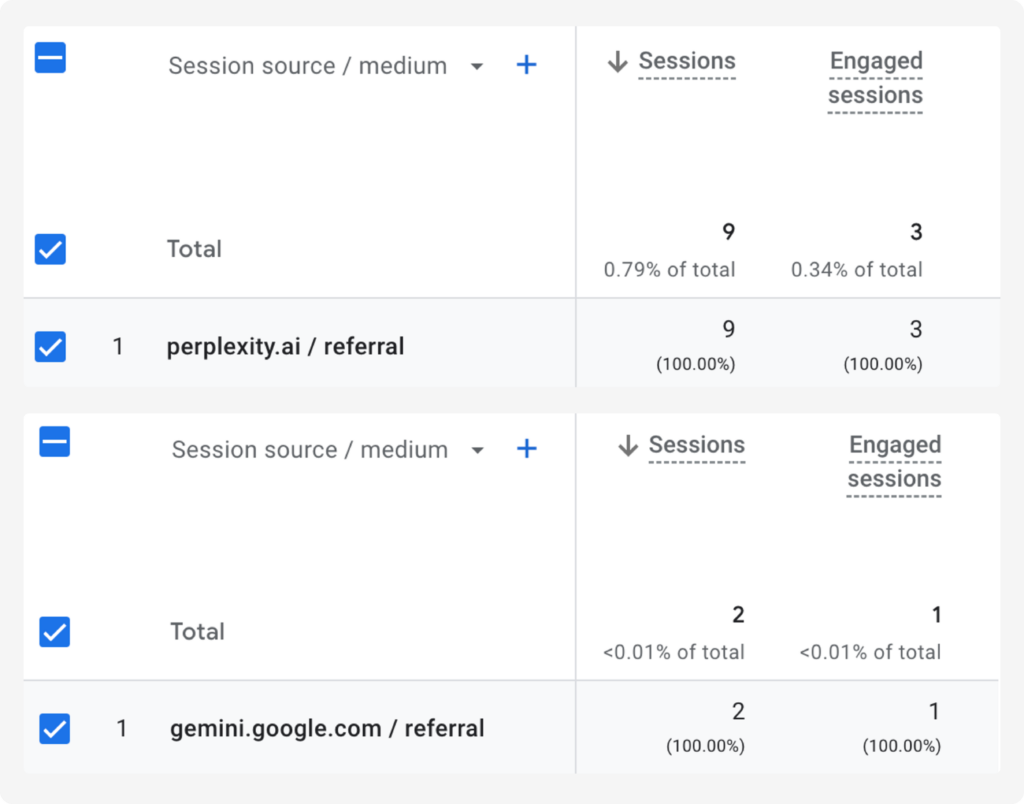
*Bing is an exception in this regard (more about this in the section on log analysis below).
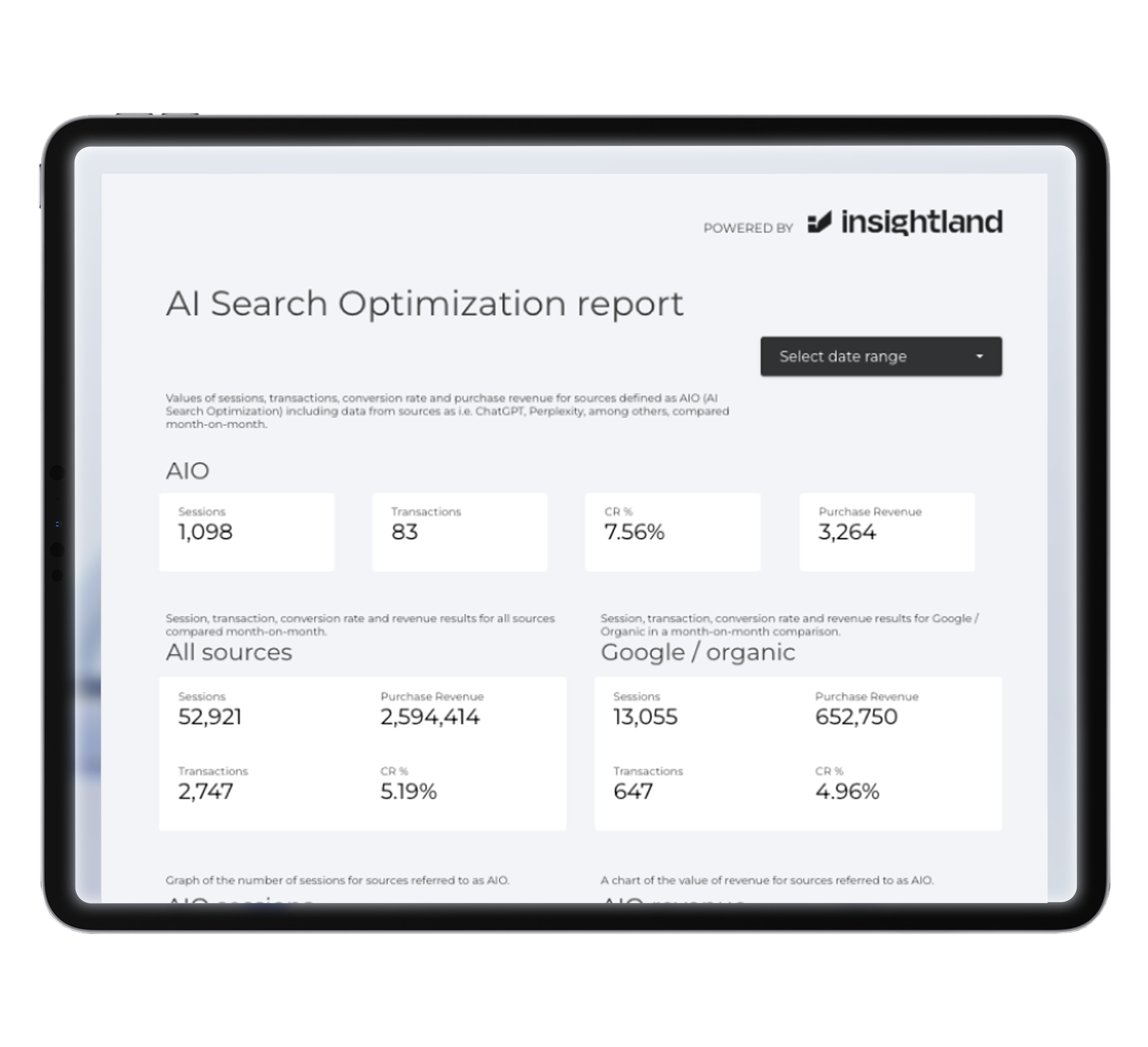
Free Looker Studio report by Insightland
At Insightland, we work with data every day. Measuring the effectiveness of our activities is crucial for us. That’s why we have prepared a free Looker Studio report with data from AI Search.
Here’s a sample view from the report:
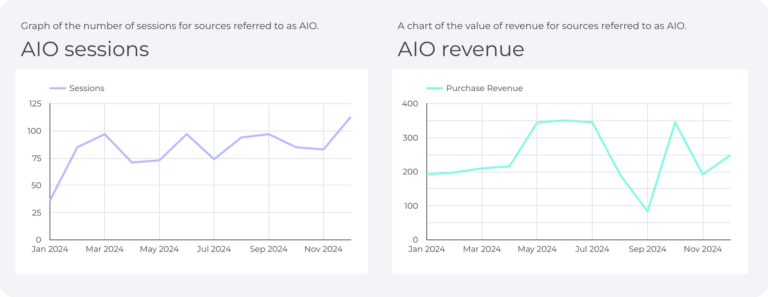
What do you get from chatbot and AI Search data analysis in GA4?
01 Understanding traffic sources
GA4 analysis allows you to identify which AI Search platforms (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, etc.) are driving traffic to your website. According to research by Ahrefs, the largest AI traffic comes from ChatGPT, Perplexity and Gemini. Awareness of these proportions allows you to adapt your optimization strategy to the most popular sources.
02 Assessment of impact on sessions
Monitoring sessions in GA4 allows you to assess how traffic from AI Search affects user engagement, time spent on the site and bounce rate. This, in turn, allows you to assess the quality of traffic and its potential impact on conversions.
03 Measuring the impact on revenue
Integrating data from GA4 with revenue data allows you to determine the extent to which traffic from AI Search translates into real profits. This is crucial for assessing the ROI in AI Search optimization.
How to use Looker Studio and GA4 reports to measure chatbot data?
Download the free report
We have prepared a free Looker Studio report template that helps you analyze the impact of generative chatbots on your business.
Analyze traffic sources
The report allows you to identify traffic sources, including AI Search platforms, that generate the most sessions on your website.
Measure the impact on revenue
Integrate revenue data to assess the extent to which traffic from AI Search translates into real profits for your business.
Track changes over time
Analyze changes in key metrics over time to assess the effectiveness of your optimization efforts and identify trends.
Sample metrics to track
- AI Search sessions: Number of sessions that originate from AI Search platforms (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, etc.).
- Conversion rate with AI Search: The percentage of AI Search sessions that resulted in a conversion (e.g. purchase, registration, form completion).
- Revenue from AI Search: Revenue generated by sessions that originate from AI Search platforms.
In the era of growing popularity of AI chatbots, monitoring and analyzing the traffic they generate becomes crucial. Standard tools such as Google Analytics 4 (GA4) may not provide the full picture, though. Therefore, it is worth using advanced methods, such as server log analysis.
Server log analysis: the key to the whole picture
The available data platforms currently don’t show us the whole spectrum of the data about traffic coming for AI search. Analysing the server logs may help us discover some interesting details necessary to start a valuable AI search traffic analysis.
What are server logs?
Server logs are records of all activities and events that occur on the server. They contain information about IP addresses, referrer, visit time, HTTP code and User-Agent. Thanks to them, we can thoroughly monitor traffic, diagnose problems, and increase website security.
How to use server logs to analyze traffic from ChatGPT?
Identifying OpenAI bots: OpenAI uses several crawlers with distinct functions that identify themselves through User-Agent. In the context of measuring visibility in ChatGPT, it is crucial to analyze logs for the presence of the ChatGPT-User bot.-User bot.
ChatGPT-User: Querying this bot in the server logs for a specific URL means that the link to that URL was displayed as a source in the ChatGPT response.
Calculating the CTR rate: Log analysis allows you to calculate the approximate CTR (Click-Through Rate) for links displayed in ChatGPT.
OpenAI bots and their User-Agent
OAI-SearchBot: Crawls pages to SearchGPT search results.
GPTBot: Searches content to train AI models. Blocking GPTBot in the robots.txt file prevents the website content from being used for AI training.
ChatGPT-User: Visits pages to help answer the GPT Chat and include a link to the source.
It’s worth mentioning that:
One URL may be specified as a source several times in one ChatGPT response, but this only corresponds to one request to the server.
Log analysis will not indicate whether the link to the website appeared directly in the response or only after clicking on “Sources”.
The logs may show what GA4 doesn’t
For instance, GA4 may not show the correct scale of traffic from chatbots, e.g. due to Consent Mode. Additionally, GA4 only shows “visits” to the site (sessions and users), not “views”, i.e. moments when a link to the site appears in the ChatGPT response. That’s why using server logs could be a game changer.
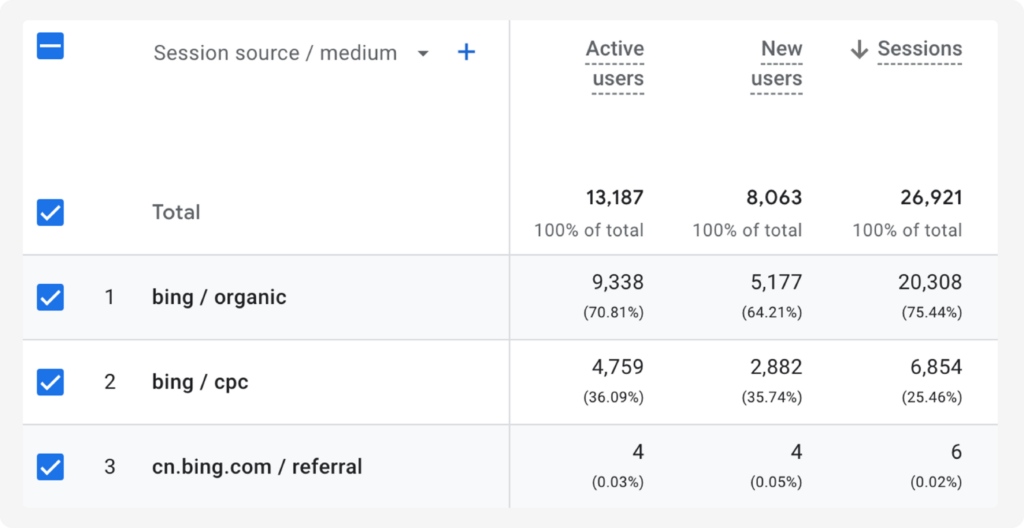
Another example, described in the Ahrefs study, shows that traffic from Copilot is recognized as Direct.
From our own experience, reports for our clients do not show the source as Bing other than standard organic/paid traffic or referral traffic from cn.bing.com. Below you’ll find the data from the last 28 days for one of our clients:
Conclusion
As AI chatbots continue to gain traction, the traffic they generate is becoming an increasingly valuable source to understand and leverage. While current measurement tools may fall short in precision, a thoughtful combination of data from the currently available tools can still provide useful insights.
For those ready to go deeper, more advanced techniques like server log analysis offer a clearer view – but they do require a higher level of technical expertise.
If you’re looking to take that first step toward understanding and optimizing your AI chatbot-driven traffic, at Insightland we can help bridge the gap and get you started with the AI search analysis.



