How to rank in Chat GPT? [2025]
There are five key insights you need to understand about ChatGPT to craft an informed strategy for AI search optimization. In this article, we break down each insight and introduce the CAT framework: a practical approach designed to boost your chances of ranking within ChatGPT results.

ChatGPT is no longer just a novelty – it’s becoming a real source of traffic for our clients’ websites. With over 1.4 billion visits each month, it’s where users discover brands, search for product recommendations, and solve problems – often before they even open Google.
The good news? We know how to get ChatGPT to recommend your business. The not-so-good news? Your competitors want the exact same thing.
So the real question is: how do you become the brand that gets featured – and maximize the value of the work you’ve already done?
From this article, you’ll learn:
1. How ChatGPT works – 5 key insights
a. ChatGPT’s view of the internet comes from Bing, not Google
b. What you see isn’t always what ChatGPT sees – JavaScript content is often invisible to the chat
c. Brand touchpoints matter – because ChatGPT remembers them
d. ChatGPT isn’t just text. It’s images, audio, and context.
2. How to rank your website in ChatGPT
b. Content
c. Authority
d. Technology
How ChatGPT works – 5 key insights
Understanding how ChatGPT works is the first step to building your brand’s visibility in the AI-driven world. ChatGPT doesn’t function like a traditional search engine. It doesn’t crawl the internet in real time for every query. Instead, it pulls data from three main sources:
- its internal knowledge base,
- Bing search results, and
- the user’s past interactions.
,,Language models don’t understand the internet – they synthesize it.”
– Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, during a discussion on the future of generative AI.
For us, that means one thing: your brand doesn’t need to be everywhere – it needs to be in the right place and in the right format.
That may sound abstract at first, but once you understand how ChatGPT thinks, it becomes a lot more straightforward.

ChatGPT’s view of the internet comes from Bing, not Google
This is one of the biggest misconceptions. When ChatGPT is in browsing mode, it doesn’t search Google – it pulls results from Microsoft’s Bing Search API. And that changes everything.
| Simplifying, the situation is like this: If your content is indexed in Bing, it can show up in ChatGPT’s responses. That means you’re not just optimizing for Google anymore. You need to think in terms of Bing – because Bing is what feeds ChatGPT. |
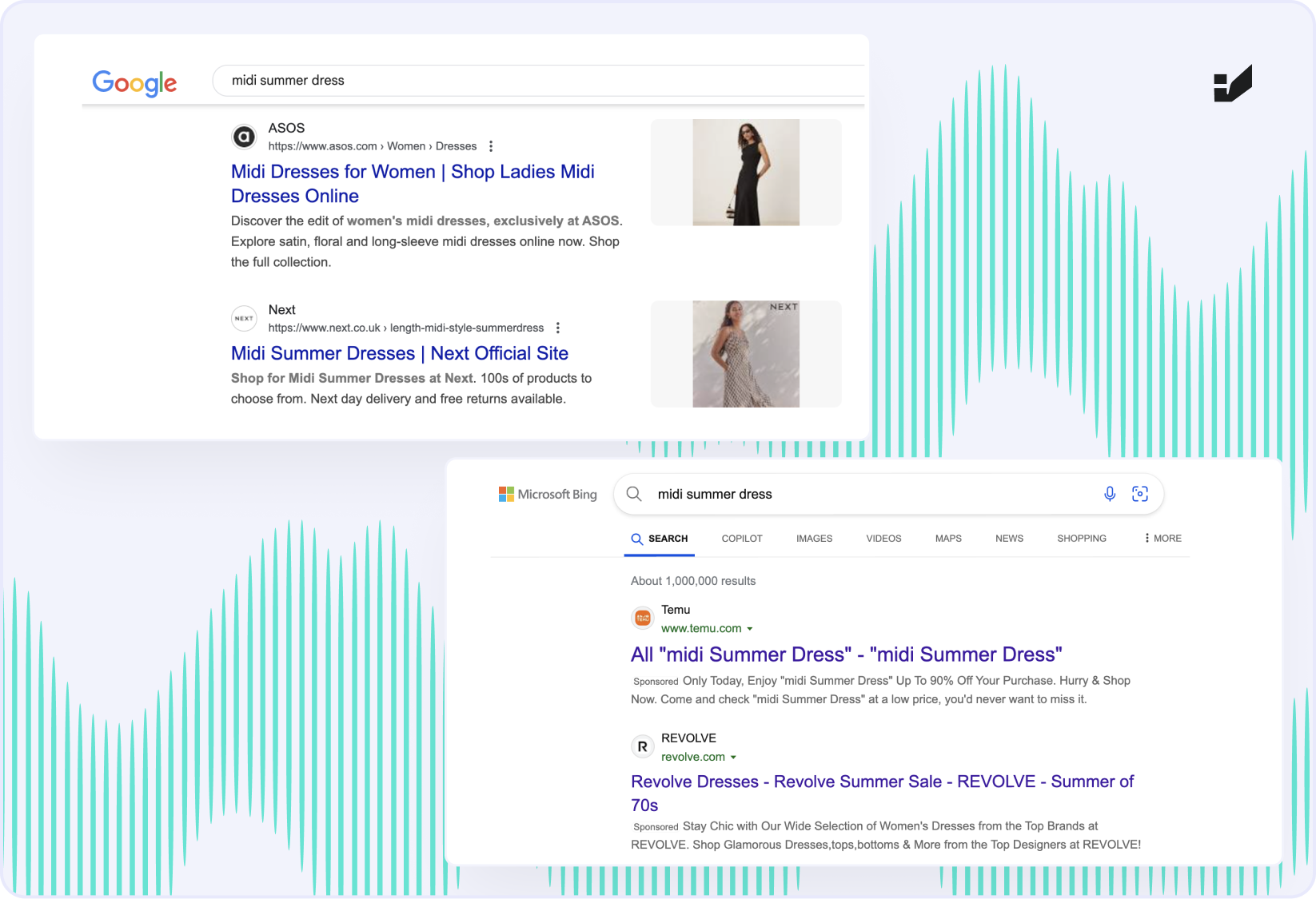
I often hear, ,,Bing is just a tiny slice of the market – it’s not relevant for my brand.” But that couldn’t be further from the truth. If your website, blog post, product page, or social media content doesn’t show up in Bing, then chances are – it doesn’t exist for ChatGPT.
What’s more, Bing uses a different ranking algorithm than Google. So even if you’re performing well in Google search, it doesn’t guarantee visibility in ChatGPT results.
| Ranking factor | Bing | |
| Keywords | Focuses on semantic search and understanding user intent and context. | Emphasizes keyword matching and intent, often powered by OpenAI models. |
| Backlinks | Prioritizes the quality, diversity, and authority of referring domains. | Puts more weight on quantity and domain type (e.g., .edu, .gov). |
| Technical SEO | Requires fast, mobile-friendly, secure websites with clean HTML and schema. | Values structured content for rich results (e.g., answer boxes). |
| On-page SEO | Looks at topical completeness and relevance over exact keyword matches. | Favors traditional optimization: title tags, headings, meta descriptions. |
| Mobile SEO | Uses mobile-first indexing (mobile version is prioritized). | Uses a single index across both desktop and mobile. |
| Social Signals | Claims social signals don’t directly impact ranking. | Considers social engagement as a ranking factor. |
| Key takeaways: > Make sure your key content is indexed in Bing Webmaster Tools. > Build a strong presence in social media – not just for users, but as a ranking signal. > Use tools like Bing URL Submission API to speed up indexing and reflect updates faster. |

What you see isn’t always what ChatGPT sees – JavaScript content is often invisible to it
ChatGPT doesn’t work like your Chrome browser. It doesn’t “click” around, wait for a page to load, render animations, or execute JavaScript. Just like most search engine crawlers – especially Bing – it doesn’t read dynamically generated content. If your most important information only appears after JavaScript loads (for example, through React or similar frameworks), ChatGPT simply won’t see it.
| In short: you can have amazing content, but if it’s hidden behind layers of technology, ChatGPT will be blind to it. |
Why does energy matter here? Operating large language models like ChatGPT isn’t just a computational challenge – it’s an energy-intensive one. Every additional task – whether it’s rendering complex layouts, executing JavaScript, or interpreting animations – draws more power. And when you’re serving millions of users in real time, every watt matters.
That’s why LLMs like GPT-4 are designed to keep things lean. They simplify how they “read” the web: no clicking, no waiting, no rendering. Just raw, accessible content.
As Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, pointed out at the World Economic Forum 2024:
This can’t be done without an energy breakthrough.
In other words: scaling AI to the next level – and making it fast, reliable, and affordable – means avoiding heavy processes like dynamic rendering. So if your site hides key content behind JavaScript or complex frameworks, ChatGPT probably won’t see it. Keep in mind that AI models need to limit what they process – and prioritize simplicity over complexity – so your job is to make that as easy as possible.
That’s where practical tools come in.
One solution we successfully implement with our clients is the LLMs.txt file – a new standard inspired by robots.txt.
This file helps you explicitly define:
- which parts of your site should be visible to large language models (LLMs),
- where your most valuable textual content lives,
- and how to surface content that might otherwise stay hidden behind scripts or frameworks.
If models like GPT-4 are built to avoid expensive rendering, the best thing you can do is guide them toward what really matters. LLMs.txt is one of the most effective ways to do just that.

| Key takeaways: > AI doesn’t see the web like humans do – it reads raw, structured content, not what appears after clicks or animations. > Content hidden behind JavaScript, dropdowns, or carousels is likely invisible to ChatGPT. > Design for machines first: prioritize HTML over heavy frameworks, and simplify access to key information. > Use tools like LLMs.txt to guide AI models directly to the most important parts of your site – and ensure nothing valuable gets lost in the code. |
ChatGPT Operates in two modes – and that changes everything for your brand visibility
When you ask ChatGPT for recommendations – like “What dresses should I wear to a summer wedding?” – it doesn’t work like Google. It doesn’t always search the internet in real time. Instead, it operates in one of the two distinct modes:
Mode 1: The Large Language Model (LLM) – pre-learned knowledge
In this default mode, ChatGPT relies solely on the data it was trained on. It does not pull fresh information from the web. Instead, it generates answers based on:
- Publicly available content (e.g. blog posts, product descriptions, articles, forums)
- Licensed datasets (from OpenAI’s partners)
- Human-reviewed training content (sample conversations, curated responses)
The result?
If your brand, products, or expertise were part of that training material – ChatGPT might mention or recommend you. But if not? You are likely to be invisible.
Example:
User asks: “What are the most popular dresses for weddings this season?”
ChatGPT responds: “Midi dresses in soft pastels are trending.”
But it won’t mention your new collection – because it doesn’t know it exists. Not yet, anyway. Thankfully, newer versions of the model rely more and more on real-time data.
Mode 2: Browsing – real-time access via Bing
When browsing mode is enabled (in Pro versions or GPT-4o by default), ChatGPT can search the web in real time using Bing. It does this when:
- the model detects the need for current or dynamic information (like prices, news, or product launches),
- browsing is active and permitted,
- the content is indexed in Bing and accessible in a clean, readable format (HTML, not JavaScript-heavy).
In this mode, ChatGPT can fetch actual products, links, and quotes from up-to-date sources – but only if they’re properly indexed and easy to parse.
But what if outdated content was already “learned” by the model?
This is a valid concern – and an important question. If something made it into the training data, does it stay there forever?
Good news: it doesn’t.
- Models like GPT-4 are updated periodically – each new version includes fresh content and insights.
- Optimized, well-indexed content has a high chance of making it into future model updates.
- And in browsing mode, you can influence responses immediately – no need to wait for the next model cycle.
ChatGPT increasingly leans on browsing for relevance and trustworthiness – which means you can shape what it sees starting today.
| Key takeaways: > ChatGPT works in two modes: pre-trained (LLM) and real-time (Browsing). > If your content isn’t in Bing or part of its training data, it won’t show up. > Browsing mode allows real-time visibility – but only for content that’s indexed and easy to read. > You can influence ChatGPT today by optimizing your content for Bing. |
Brand touchpoints matter – because ChatGPT remembers them
Most people still think of AI like a search engine:

But that’s not how ChatGPT works. It builds context – and unless memory is turned off, it remembers what the user previously engaged with.
That means if a user has:
- asked about your brand,
- mentioned it in a conversation,
- opened a link or read content you’ve published,
- uploaded a product image or asked about your category…
…then ChatGPT may start treating your brand as “known” or even “preferred.”
In future queries – even unrelated ones – your brand is more likely to show up.
What does that mean for SEO and AI visibility?
It’s a fundamental mindset shift.
Traditional SEO focuses on the bottom of the funnel – sales-driven keywords. But in the ChatGPT world, every touchpoint counts. Even early-stage interactions – education, inspiration, comparisons – increase your chance of being recommended later. And not just once, but repeatedly, as memory builds.
Yes, OpenAI allows users to disable memory – but very few actually do. By default, memory is on. Which means:
A single touchpoint today can become a recommendation tomorrow.
In this new landscape, SEO is no longer just about position – it’s about recognition and recall.
| Key takeaways: > Be present across the entire customer journey – not just at the decision stage. > Create content that encourages interaction – clicks, questions, conversations. > The more often users engage with your brand, the stronger your footprint becomes in ChatGPT’s memory. |
ChatGPT isn’t just text. It’s images, audio, and context.
ChatGPT is no longer limited to text-based prompts. Thanks to multimodal capabilities, it can understand images, audio, and other formats – all within the same conversation.
What does that mean for your brand?
A user can upload a product photo, reference a chart from a report, or ask a question via voice – and ChatGPT can interpret that information and respond accordingly.
It’s not magic. It’s a result of the model processing multiple data types and synthesizing them into a coherent output – whether that’s a written response, a DALL·E-generated image, or a voice recommendation.
From an optimization perspective. Your brand can no longer rely on one content format alone. Visual assets (like charts or infographics), audio materials (like podcasts), and even structured documents (like PDFs) can become part of the user’s prompt.
But here’s the nuance:
There’s a difference between what a user brings into a chat, and what the model knows about your brand from public data.
Even the most advanced models, like GPT-4o, don’t actively browse your website or watch your videos. They process content based on structure – not human vision or intuition.
So, if a video or graphic on your site doesn’t include a description, transcript, or context, it may as well not exist from the model’s perspective.
Your visibility in AI isn’t just about having a website. It’s about how well your content is structured, described, and accessible across formats users can reference – whether they speak it, upload it, or paste it into a prompt.
If you’re not present across those formats – or if your content lacks interpretive context – the model has nothing to pull from.
And if you want to be sure the model connects that content to your brand and interprets it correctly – host it on your site and provide the right context.
| Key takeaways: > Try to place images and videos on your own site, with descriptions and context. > Optimize for Bing: include clear titles, meta tags, and structured data. > Add relevant keywords around embedded media. > Use alt text to help models interpret visual elements correctly. |

So now that you know how ChatGPT works – the question is, how do you get your brand to show up in it?
Understanding the mechanics is one thing. Designing your content, authority, and tech for AI visibility is another. That’s where our CAT framework comes in.
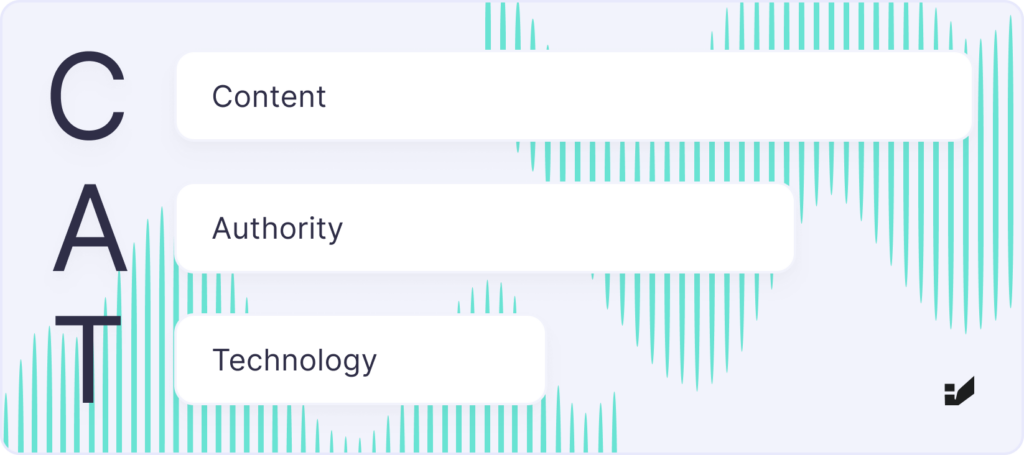
How to rank your website in chatGPT: the CAT framework
If ChatGPT is the new search engine, then it calls for a new approach to SEO.
The CAT framework is a strategic model that helps you understand how to prepare your brand for visibility inside AI-driven conversations. It doesn’t replace traditional SEO – it complements it. And it doesn’t require a revolution – just a smart evolution.
CAT stands for Content, Authority, and Technology – in that exact order.
Why this order? Because in the world of AI, it’s not links or metadata that come first – it’s your content. Then comes trust. And only then, the technical layer. That’s exactly how ChatGPT works.
C – Content
Let’s start here – with content.
Did you notice something about this article? It’s written like we’re having a conversation. That’s not a coincidence.
It’s because ChatGPT isn’t just looking for information – it’s looking for language it can talk with. And that changes everything. The better your content mirrors natural conversation, the more likely it is to be picked up, understood, and used by the model in real answers.
In AI-driven search, your content isn’t scanned – it’s synthesized. That synthesis favors clarity, intent, and structure that feels human.
- Answer real user questions (FAQ-style, intent-based)
Language models like ChatGPT are trained on massive datasets filled with questions, answers, and conversational prompts. That’s why content that mimics a natural human interaction is far more likely to be understood-and cited-by the model.
So what kind of content does that mean for you?
You should create content that’s:
- Based on real user questions (from Search Console, chats, forums, etc.)
- Easy to quote in full: clear, complete answers in natural language
- Framed around intent: titles like “How to…”, “Is it worth…”, “What does… mean?”
In short: make it conversational and contextual.
Not LLM-friendly:
“Our accounting office offers comprehensive services for companies and sole proprietorships.”
LLM-friendly example:
“If you’re looking for a trusted accounting office in Wrocław, consider using our services. We specialize in working with sole traders, managing ledgers, and providing tax advice. We also support company registration and cost optimization.”
- Use language that’s syntactically and semantically clear
ChatGPT doesn’t read between the lines. It processes text token by token and builds meaning based on syntax and structure. That means:
- avoid overly complex or nested sentences,
- use proper nouns, classifiers, and descriptive adjectives (e.g. “water-soluble vitamin C”),
- make sure every paragraph contains a full thought and context on its own.
- Build relationships between entities
What Google once called “semantic search” now becomes “entity linking” in the world of large language models. Entities are real things the model can recognize: your brand, your product, a location, ingredient, problem, or category.
Models learn by pattern repetition. The more consistently your brand is linked to a topic, the more likely it is to become the “default” for that subject in ChatGPT’s responses. That’s why you need to build not just content, but also the contextual connections between key entities.
Example: Just mentioning “vitamin C” isn’t enough. But if your content consistently links “vitamin C” + “serum” + “sensitive skin” + “Brand X”, you’re teaching the model to associate those ideas with your brand.
Instead of:
“Our serum contains vitamin C.”
Try:
“This vitamin C serum helps reduce dark spots and is gentle enough for morning use. Great for sensitive skin.”
Remember: Entities aren’t a guessing game. They’re measurable, trackable, and optimizable. We use proprietary tools and frameworks to help our clients shape and reinforce entity-based content.

- Build content around topical authority
Writing one article about SEO doesn’t make you an authority. Language models understand topic expertise based on:
- Breadth (do you cover the full landscape?)
- Depth (do you break topics into subtopics?)
- Internal and external linking (semantic associations, citations, consistent language)
Technically speaking, the closer your content gets to a “knowledge graph” structure, the more likely ChatGPT is to notice and use it.
- Publish in places models can access
Even the best content is useless if it’s invisible to the model. This applies not only to what’s published on your own site, but also to outreach efforts and external content that helps establish those entity connections. Make sure that pages are:
- published on high-authority domains (PR outlets, LinkedIn, expert blogs),
- not hidden behind JavaScript,
- enhanced with structured data (schema.org),
- internally linked and thematically grouped (use topic clusters or silos).
A – Authority (brand and content authority)
In traditional SEO, authority is often associated with backlinks and traffic. In AI-driven search, it’s something deeper: whether a language model considers your brand or content worth citing in a response to a user. It’s not the result of a single article, but the outcome of a broader network of signals you build around your expertise and semantic visibility.
How does ChatGPT “see” authority?
LLMs don’t evaluate domain reputation the way search engines do. Instead, they assess:
- the consistency and repetition of the context in which your brand appears (topical authority),
- the volume and quality of mentions in trusted sources (media outlets, expert blogs),
- strong semantic ties to specific topics (topical consistency),
- the clarity and reputation of entities in the training data.
So what should you focus on?
- Appear in media, earn citations, and participate in PR, podcasts, and interviews.
- Build relationships with relevant entities (e.g., “best supplements → your brand”).
- Maintain thematic consistency across your content (specific problems, niches, or categories).
- Get featured in third-party sources that validate your expertise (rankings, case studies, reviews).
- Stay present in social media – especially in open, indexable groups or discussions.
- Use structured data (schema.org) with attributes like Person, Organization, Author, and sameAs.
- Structure your content using thematic silos (also known as topic clusters).
T – Technology (accessibility, indexability, AI-readiness)
If your website is already technically optimized for Google – great! That means you’re probably closer to the AI-search optimization standards than you think. In many cases, only a few key adjustments are needed to meet the expectations of modern language models like ChatGPT.
As mentioned earlier, these models don’t interpret JavaScript, don’t wait for content to load, and don’t navigate complex frontend frameworks. That means content buried in dynamic components, dropdowns, or carousels is effectively invisible.
AI doesn’t need animations or beautiful transitions – it needs clean, structured data it can process at scale.
Here’s how to bridge the gap between “Google-ready” and “LLM-ready”:
- Use server-rendered HTML or make key content available outside of JavaScript.
- Add an LLMs.txt file to guide AI models toward your most important content.
- Mark up your site with structured data (schema.org) – for clarity, not just SEO.
- Optimize for Bing (metadata, headings, page speed, social validation).
- Provide accessible elements: transcripts, alt text, clean hierarchy.
Monitor your server logs – they’re your best ally in understanding if and when ChatGPT-related bots are crawling your site. Make sure those bots actually have access.
The more easily machines can read your content, the more likely your brand is to appear in AI-generated answers. In a world of ever-expanding digital interfaces, simplicity is power.
After reading this article, you now know a lot more than most. Most importantly, you’ve realized that ChatGPT is no longer just a novelty.
It’s a real source of traffic. A place where users discover products, ask for recommendations, and make decisions – often before they even open Google.
![Banner with text: Wondering what ChatGPT says about your brand?
Get a free, expert-crafted audit of your AI search presence. [Request your audit] Click if you want to go to the free audit landing page.](https://insightland.org/app/uploads/2025/05/Insightland-AI-Search-Optimization-1-1024x323.png)
The good news? You already have content, authority, and technology in place. Even better news? With the right approach, you can turn it all into visibility in AI-generated answers.
That’s exactly what our AI Search Optimization helps you do.
We work at the intersection of SEO, AI, and conversational data – making sure your brand gets found, understood, and recommended by the most powerful models in the world.
Curious what that could work for your business? Let’s talk.



